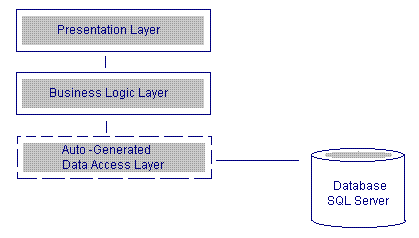
Introduction
Data Access Layer (DAL) is an important part in almost all architectures. I encountered problems creating DAL for large databases — maintaining DAL for these databases was another nightmare. So I thought of a generic solution to this problem, which was to auto generate the DAL.
I made use of System.CodeDom which is a code generator to produce source code in a particular programming language.
Using the Code
In order to generate DAL in your ASP.NET project follow the below steps:
- Add a reference of DalProvider.dll which is a DAL Auto-Generator Library
- Add the following under compilation tag in the web.config
 Collapse | Copy Code
Collapse | Copy Code <system.web>
<compilation debug="true">
<buildProviders>
<add extension=".dal"
type="AnoopsDALGenerator.DalProvider"/>
<buildProviders>
</compilation>
</system.web>
This allows the compilation of any file with the ".dal" extension added to the project with our DAL auto generation library.
- Add a XML file to the App_Code folder in the below mentioned format with the extension ".dal"
 Collapse | Copy Code
Collapse | Copy Code <dal>
<connectionString>Data Source =XXXXX; Initial Catalog = XXXXX;
User Id =XXXXX; Password=XXXXX
</connectionString>
<nameSpace>DAL1</nameSpace>
</dal>
In this XML file under the "dal" root tag we need to mention the connection string of the database as well as the namespace to access the auto generated DAL.
- Compile your ASP.NET project. This generates the DAL with the following features:
- Namespace "DAL1" as specified in the XML file
- All tables are represented as classes with its columns as member fields that can be accessed using property with name in the following pattern "Col" + Column Name. This enables the users to create objects of tables.
 Collapse | Copy Code
Collapse | Copy Code DAL1.TableName table1 = new DAL1.TableName();
tabel1.ColColumnName1 = "2";
table2.ColColumnName2 = "Trial";
Response.Write ("Data in column2:" + table2.ColColumnName2);
- All stored procedure access methods are defined under the
DataProcedure class. Thus to access a stored procedure the user has to use the respective stored procedure access function ("Access"+StoredProcedureName).
 Collapse | Copy Code
Collapse | Copy Code DAL2.DataProcedure dbObject = new DAL2.DataProcedure();
DataTable dataResult=new DataTable();
int returnStatus = dbObject.AccessStoredProcedureName(ref dataResult,
"21", "Thomas", "Atlas", "ITDept");
if (returnStatus>
A reference to a datatable has to be passed to this function to retrieve the records fetched using the stored procedure.
Code
The code is big but simple. The work flow of this library is as below:
- Extract the connection string and the proposed namespace from the XML file during compilation
- Query the
systemobjects table and systemcolumns table to list out the tables and columns respectively
 Collapse | Copy Code
Collapse | Copy Code
Select * from sysobjects where type = 'u'
Select * from syscolumns
- Generate classes from the table names and create coulmns as member variables under it
- Create a class named
DataProcedure to hold the functions to access stored procedures
- Query the
systemobjects table to list all the stored procedures
 Collapse | Copy Code
Collapse | Copy Code Select * from sysobjects where type = 'p' and category = 0
- Query
systemcolumns to get the parameters of the respective stored procedure
 Collapse | Copy Code
Collapse | Copy CodeSELECT
param.name AS [Name],
ISNULL(baset.name, N'') AS [SystemType],
CAST(CASE WHEN baset.name IN (N'char', N'varchar', N'binary', N'varbinary',
N'nchar', N'nvarchar')
THEN param.prec ELSE param.length END AS int) AS [Length],
CAST(param.xprec AS int) AS [NumericPrecision],
CAST(param.xscale AS int) AS [NumericScale],
null AS [DefaultValue],
CAST(
CASE param.isoutparam WHEN 1 THEN param.isoutparam WHEN 0 THEN
CASE param.name WHEN ''
THEN 1 ELSE 0 END END AS bit) AS [IsOutputParameter]
FROM
dbo.sysobjects AS sp
INNER JOIN sysusers AS ssp ON ssp.uid = sp.uid
INNER JOIN syscolumns AS param ON (param.number = 1) AND (param.id=sp.id)
LEFT OUTER JOIN systypes AS baset ON baset.xusertype =
param.xtype and baset.xusertype = baset.xtype
WHERE
(sp.xtype = N'P' OR sp.xtype = N'RF')and(sp.id= ? and ssp.name=N'dbo')
ORDER BY
CAST(param.colid AS int) ASC
- Combine all the information and generate functions to access stored procedures
Points of Interest
This solution is a good example of using System.CodeDom.